The Swift logging framework.
Atlantis is an extremely powerful logging framework that I've created for everyday use, including enterprise development for aspiring start-ups or for rapid prototyping API's. It is type agnostic, meaning you can pass in anything from strings to customobjects that you yourself made... and it will basically pretty print all the values within that object or literally anything in general. It is made with exceptional readability and ease of use.
Installation
Add this to your podfile...
# for Swift 4.0
pod 'Atlantis', :git => 'https://github.com/aaronjsutton/Atlantis.git', :branch => 'swift-4-patch'
# for Swift 3.0
pod 'Atlantis'
# for Swift 2.3
pod 'Atlantis', :git => 'https://github.com/DrewKiino/Atlantis.git', :branch => 'swift2.3'
Then do a pod install, and voila!
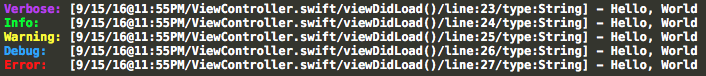
Unique Logs
This includes the stamp trace of the log's date, source, function, line number, as well as the actual type of the value.
Note: The date's format goes by month, date, year, hour, then time of day.
// You do not need to initialize this, the variable is initialized in file.
let log = Atlantis.Logger()
// Let's log some stuff
log.verbose("Hello, World!")
log.info("Hello, World!")
log.warning("Hello, World!")
log.debug("Hello, World!")
log.error("Hello, World!")
Which prints the following...
Powerful Printing
Atlantis is built to pretty print literally everything.
- proper text alignment
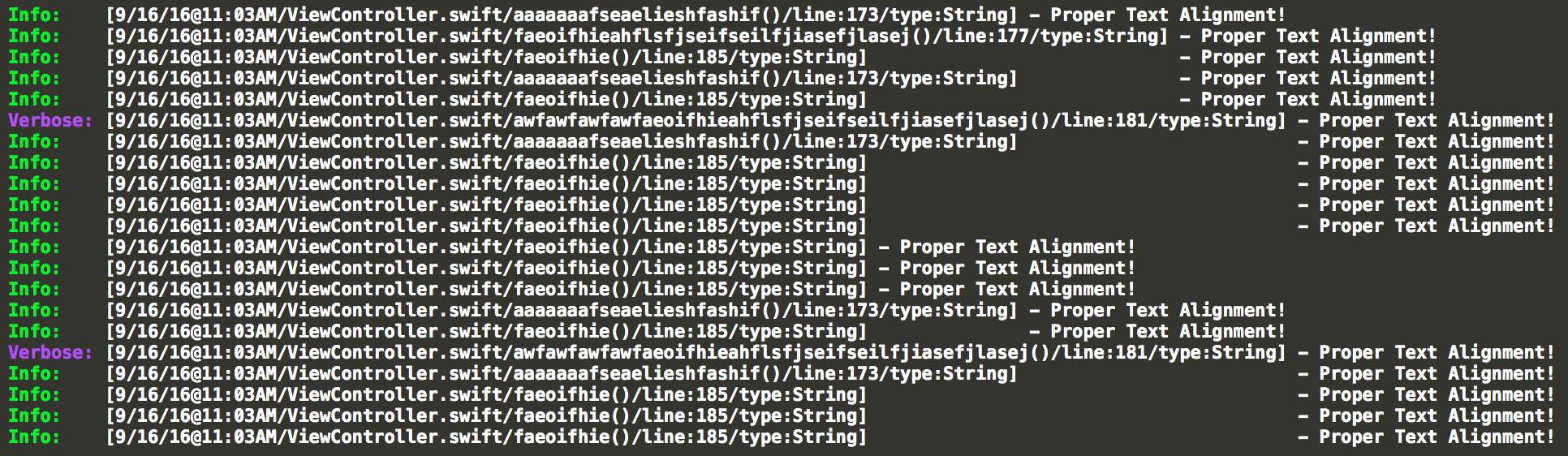
Atlantis automatically aligns its logs based on it's previous alignments. However you can change this configuration by setting this variable,
Atlantis.Configuration.alignmentThreshold
which defaults to 5.
- optionals
Atlantis will safely unwrap any optionals.
let doIExist: String? = nil
log.warning(doIExist)
// prints 'nil'
- empty strings
Atlantis will visually print empty strings.
let emptyString: String = ""
log.warning(emptyString)
// prints ""
- native types
let string = "Hello, World"
let int = 123
let double = 12.3
let float = 12.3
let bool = true
// you can either log one value
log.debug(string)
// or all of them like so,
log.debug(string, int, double, float, bool)
// prints
"Hello, World" // first one
"Hello, World" // prints each with a new line
123
12.3
12.3
true
- arrays
// array of ints
let numbers = [123, 1234, 12345]
log.debug(numbers)
// prints
[
123,
1234,
12345
]
// lets try arrays of arrays
let numberArray = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]
log.debug(numberArray)
// prints
[
[
1,
2,
3
],
[
4,
5
]
]
- dictionaries
// on to dictionaries...
let dictionary: [String: AnyObject] = [
"quote": "It is better to have loved, than to have never loved at all?"
]
log.debug(dictionary)
// prints
[
"quote": "It is better to have loved, than to have never loved at all?"
]
// how about NSDictionary types?
var dictionary = NSDictionary()
dictionary.updateValue("will this work?", key: "question")
log.debug(dictionary)
// prints
[
"question": "will this work?"
]
// say we got two response objects from the server,
// now both objects are the same but one of them has missing data...
responses.map { log.debug($0) }
// prints
{
"response": "Here is some data!",
"success" 200
},
{
"response": null,
"success" 200
}
// Atlantis will print all of the object's keys regardless of missing
// or empty values and will print null if need be.
- objects
// now let's get to the fun part,
// native Foundation (ex: UIView, UIColor, etc.)
log.debug(UIColor())
// prints
<UIPlaceholderColor: 0x7ff1fb517ab0>
// native NSObjects
public class Dog: NSObject {
var name = "Doug"
}
let dog = Dog()
log.debug(dog)
// prints
{
"name": "Doug"
}
// But what about objects you created with no native subclasses?
public class CustomObject {
var id: Int = 123
var name: String = "Ben"
}
let customObject = CustomObject()
log.debug(customObject)
// prints
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
}
// Haha, no way?
// Alright, well how about custom objects with custom objects in them?
public class ParentObject {
var id: Int = 456
var name: String = "Tammy"
var customObject: CustomObject = CustomObject()
}
let parentObject = ParentObject()
log.debug(parentObject)
// prints
{
"id": 456,
"name": "Tammy"
"customObject": {
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
}
}
// That's right.
// Okay, custom objects with an array of custom objects. ;)
public class ParentObject {
var id: Int = 456
var name: String = "Tammy"
var customObjects: [CustomObject] = [CustomObject(), CustomObject()]
}
let parentObject = ParentObject()
log.debug(parentObject)
// prints
{
"id": 456,
"name": "Tammy"
"customObjects": [
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
},
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
}
]
}
// Not impressed?
let parentObject1 = ParentObject()
let parentObject2 = ParentObject() // one of its child has a dictionary
let parents: [ParentObject] = [parentObject1, parentObject2]
log.debug(parents)
// prints
[
{
"id": 456,
"name": "Tammy"
"customObjects": [
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
},
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
}
]
},
{
"id": 456,
"name": "Tammy"
"customObjects": [
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
},
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Doug"
"dictionary": [
"likes": "baseball",
"dislikes": "pad thai"
]
}
]
}
]
// Atlantis' logging is infinitely and ambiguously recursive,
// it supports almost all data types including arrays, dictionaries,
// and any objects within any objects. ??
- Structs
// Great!! Now on to some more stand-alone but much needed types.
struct Struct {
var name: String = "Bob the Builder"
var skills: [String] = ["structures, buildings"]
}
log.debug(Struct())
// prints
{
"skills" : [
"structures, buildings"
],
"name" : "Bob the Builder"
}
- Enum
enum ErrorType {
case Severe
case Moderate
case Casual
}
let type: ErrorType = .Severe
log.debug(type)
// prints
Severe
// one more example.
log.debug(ErrorType.Moderate)
log.debug(ErrorType.Casual)
// prints
Moderate
Casual
Error Handling
Atlantis will print all errors like so,
Error: [ViewController.swift/viewDidLoad()/line:98]
{
"code" : 404,
"localizedDescription" : "The operation couldn’t be completed. (Hello, World! error 404.)",
"domain" : "Hello, World!",
"userInfo" : {
"error": "found"
"note": "syntax"
}
}
It will automatically parse the localized description, error code, domain, and user info from the NSError object.
Atlantis.Configuration.highlightsErrors // default false
By default, Atlantis will print all logs equally in white or in color if colored logging is enabled. However, if you enable error highlighting it will always highlight errors regardless of any set parameters.
Atlantis.Configuration.filteredErrorCodes
Atlantis has the ability to filter out errors based on their error code. For example, you have a method that sends requests to the network and you made it so it can only make one request at a time so it will always cancel the last request made. However, some APIs are out of our control and will send out errors without your permission.
Say you want to filter out error code -1099 // offline error,
Atlantis.Configuration.filteredErrorCodes.append(-1099)
// let's call a method that throws errors, however one of the
// errors is something we want to filter out.
method() { error in
log.error(error) // can either be error 404 or -1099?
}
// will only print the error if the error code is 404
Now, if the method throws a -1099 error, Atlantis will will skip over it!
.Tap
Tap is an Atlantis extension that allows you to print like how you would regularly do, but will return the value of the input.
func add(x: Int, _ y: Int) -> Int { return x + y }
let addXY = log.tap.debug(add(3, 5))
// prints 8 and assigns the value to addXY
Normal extensions such as .Verbose etc. are also under .Tap
Compatible with Promises
using PromiseKit more specifically...
func promise() -> Promise<String> {
return Promise { fulfill, reject in
// blah blah
fulfill("Hello from server!")
}
}
promise()
.then { log.tap($0) }
.then { reply in
// blah blah
}
.catch { log.error($0) }
// prints "Hello from server!" while completing the promise.
Note that .Tap can only take in single inputs.
Configuration
Levels
Atlantis.Configuration.logLevel // default .Verbose
The five log levels are: Verbose, Info, Warning, Debug, Error, and None, ordered by priority.
For example, if you set the log level to Debug, Atlantis will only print logs whose levels are Debug and Error.
Setting the log level to .None means Atlantis will skip all log execution. I recommend using this when the app is shift off to production.
Source Information
Atlantis.Configuration.showExtraInfo // default true
You can also hide the source details by setting this parameter to false.
Coloring
Atlantis is able to provide full color customization,
// colors
Atlantis.Configuration.hasColoredLogs // default false
Atlantis.Configuration.hasWhiteBackground // default false
Atlantis.Configuration.coloredLogLevels // default [.Verbose, .Info, .Warning, .Debug, .Error]
// using a Tuple initializer
Atlantis.Configuration.logColors.info = Atlantis.XCodeColor(fg: (Int, Int, Int)>, bg: <(Int, Int, Int)>)
// using UIColor setting only the foreground
Atlantis.Configuration.logColors.info = Atlantis.XCodeColor(fg: UIColor)
// or using UIColor setting both the foreground and background
Atlantis.Configuration.logColors.debug = Atlantis.XCodeColor(fg: UIColor, bg: UIColor)
By default, Atlantis doesn't print its logs in colors. if you want colors, you will need to set the configuration during launch.
However, for you to enable log colors you will have to first download the xcode package manager Alcatraz and enable it inside xcode. Pull up the package manager afterwards and install XCodeColors.
Afterword
To Do
create a logging frameworkadd color customization- print to a text file when used on a device
pretty print json types from server responses