UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout
A project for studying of UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout
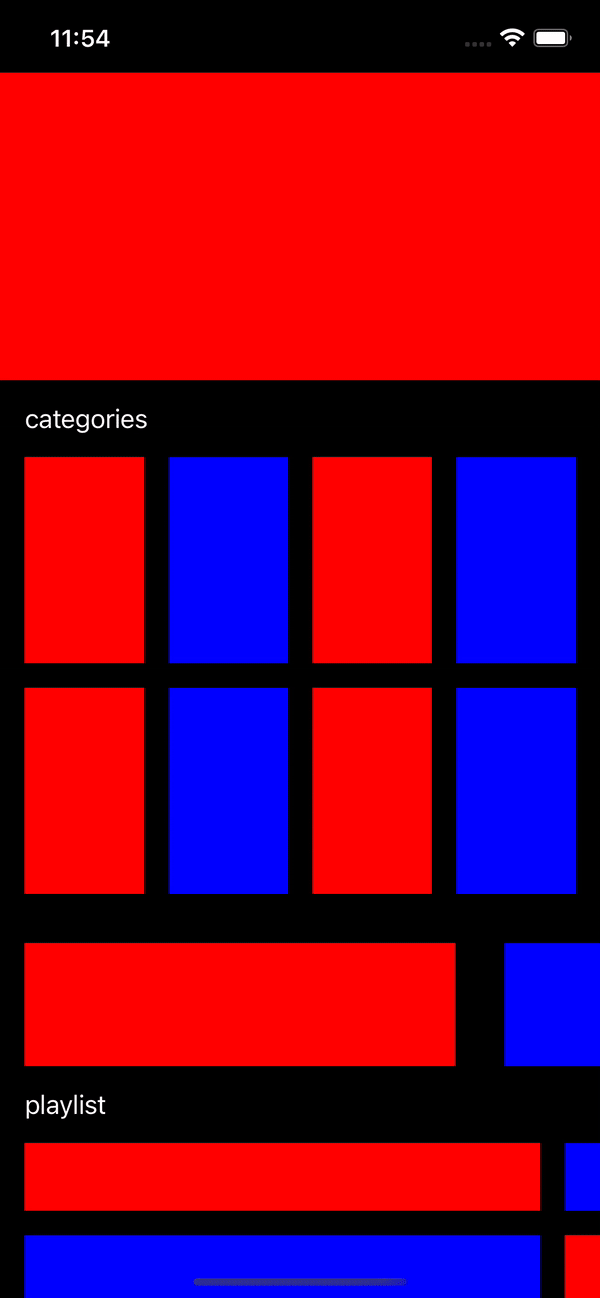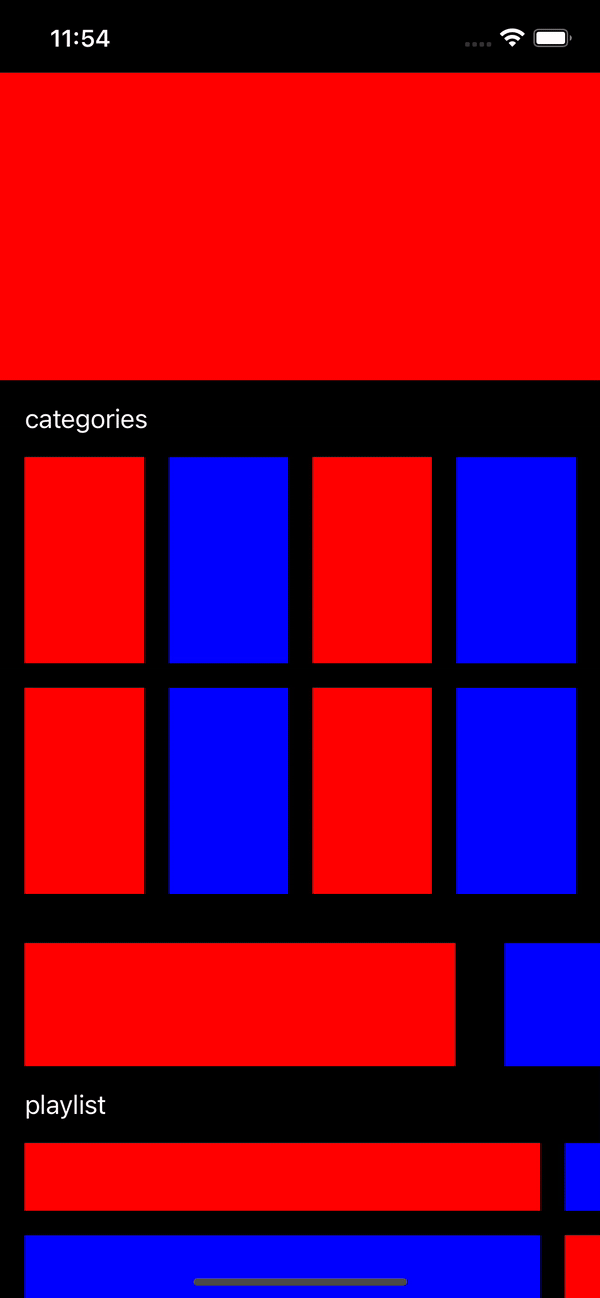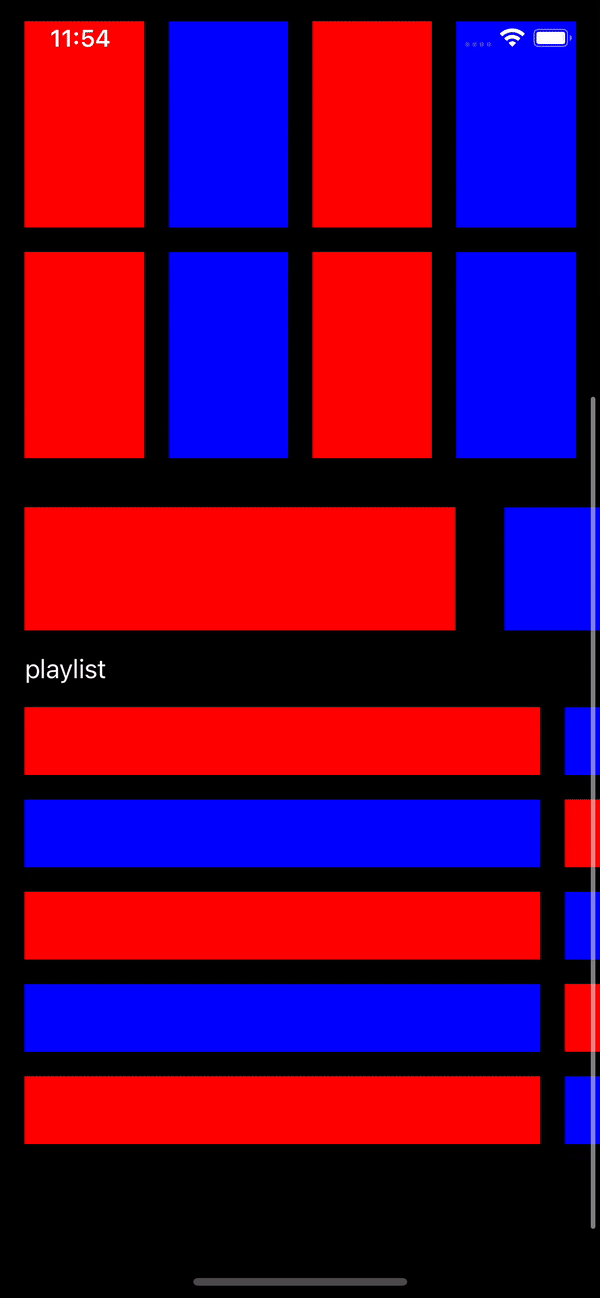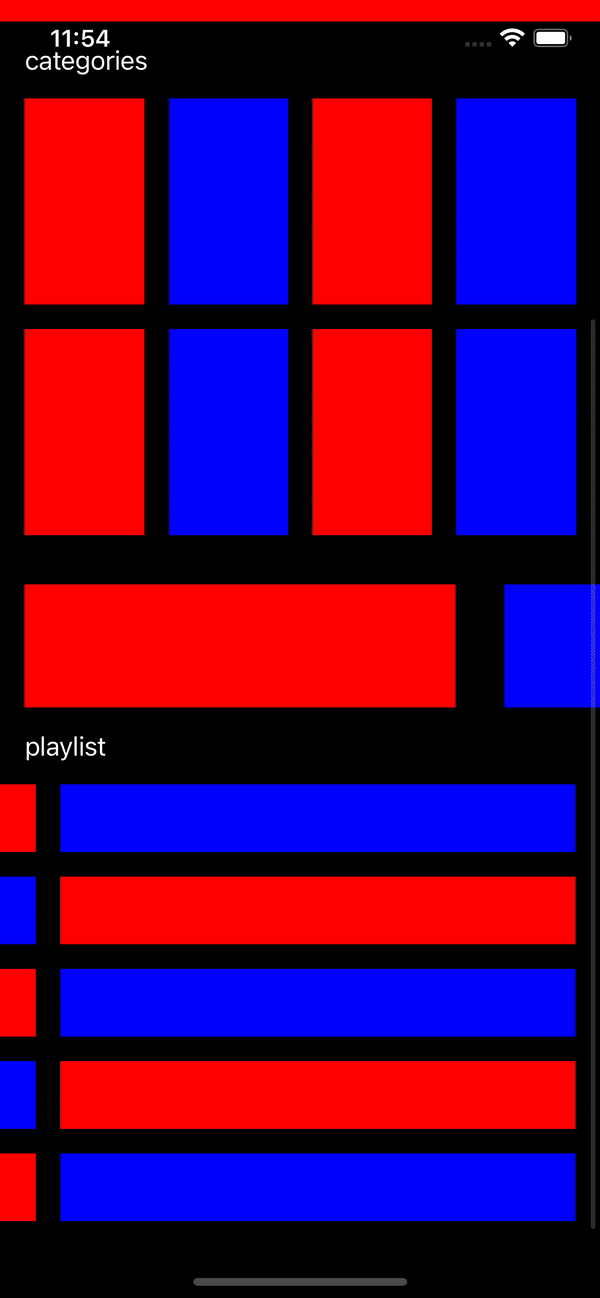
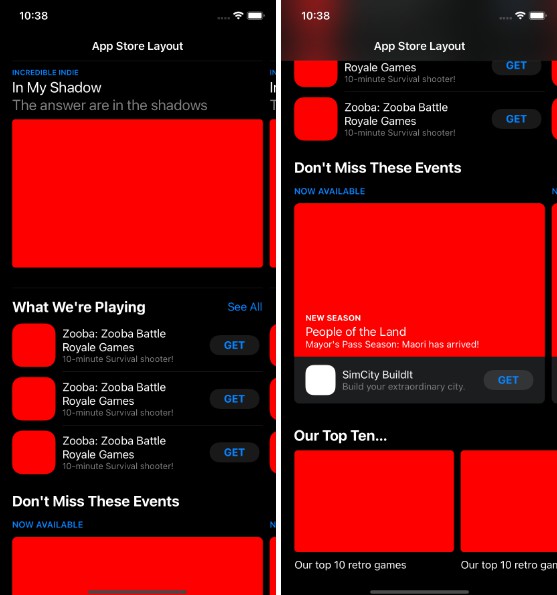
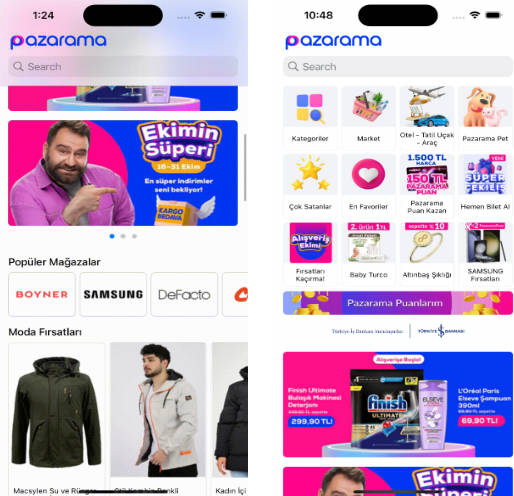
Let’s see the result of project
How will you make this layout with UIKit? Using nesting CollectionViews? It should be hard. But it’s getting simpler when you use UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout
UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout
It inherits UICollectionViewLayout. It is used to combine variety layouts. It is composed of 3 type of component
Section (NSCollectionLayoutSection)
It is a container that takes a Group. CollectionView can have one or multiple sections. Section is area of each layout. Section is determined by NSCollectionLayoutGroup. Each section can have a unique background, header, footer.
Group (NSCollectionLayoutGroup)
It is a container that takes items. It acts similar to LayoutItem because it inherited NSCollectionLayoutItem. It plays a role in placing items according to a specific path. It just places items not rendering items. It is injected into Section’s init function. It is configured it’s size by NSCollectionLayoutDimension. I will explain about this concept at below.
Item (NSCollectionLayoutItem)
It is a most basic component of CollectionView. It is a blueprint about (content’s) size, space, arrange. In general, item is a cell, but also can be a Supplementary View(ex: Headers, Footers, Decorations). It is configured it’s size by NSCollectionLayoutDimension. It is injected into the Group.
NSCollectionLayoutDimension
It determines the size of the item in CollectionView. There are 3 ways.
absolute
let absoluteSize = NSCollectionLayoutSize(widthDimension: .absolute(44), heightDimension: .absolute(44))
It renders always fixed size item.
estimated
let estimatedSize = NSCollectionLayoutSize(widthDimension: .estimated(200), heightDimension: .estimated(100))
You use estimated when the size can be updated in runtime. System calculates real size based on estimated size.
fractional
let fractionalSize = NSCollectionLayoutSize(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(0.2), heightDimension: .fractionalHeight(0.2))
I highly recommend fractional. It determines size based on the ratio based on the size of container it belong to. Possible value range is from 0 to 1.
Tip
You can check your result quickly using Preview of SwiftUI even in UIKit.
final class MyController: UICollectionViewController {
//.. My code
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
Container().edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all)
}
struct Container: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIViewController {
return UINavigationController(rootViewController: MyController())
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewControllerType, context: Context) {
}
typealias UIViewControllerType = UIViewController
}
}
Section1
let item: NSCollectionLayoutItem = .init(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .fractionalHeight(1)))
let group = NSCollectionLayoutGroup.horizontal(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .absolute(200)), subitems: [item])
let section = NSCollectionLayoutSection(group: group)
section.orthogonalScrollingBehavior = .groupPaging
return section
Section2
let item: NSCollectionLayoutItem = .init(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(0.25), heightDimension: .absolute(150)))
item.contentInsets.bottom = 16
item.contentInsets.trailing = 16
let group = NSCollectionLayoutGroup.horizontal(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .estimated(500)), subitems: [item])
let section = NSCollectionLayoutSection(group: group)
section.contentInsets.leading = 16
section.boundarySupplementaryItems = [.init(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .absolute(50)), elementKind: ViewController.categoryHeaderId, alignment: .topLeading)]
return section
Section3
let item: NSCollectionLayoutItem = .init(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .absolute(80)))
item.contentInsets.trailing = 32
let group: NSCollectionLayoutGroup = .horizontal(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(0.8), heightDimension: .estimated(200)), subitems: [item])
let section = NSCollectionLayoutSection(group: group)
section.orthogonalScrollingBehavior = .groupPaging
section.contentInsets.leading = 16
section.contentInsets.top = 16
return section
To use Group Paging, reduce size of the Group not Item.
Section4
let item = NSCollectionLayoutItem(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .fractionalHeight(1)))
item.contentInsets.trailing = 16
item.contentInsets.bottom = 16
let group = NSCollectionLayoutGroup.vertical(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(0.9), heightDimension: .estimated(300)), subitem: item, count: 5)
let section = NSCollectionLayoutSection(group: group)
section.boundarySupplementaryItems = [.init(layoutSize: .init(widthDimension: .fractionalWidth(1), heightDimension: .absolute(50)), elementKind: ViewController.playlistHeaderId, alignment: .topLeading)]
section.contentInsets.leading = 16
section.orthogonalScrollingBehavior = .groupPaging
return section
Playlist section has 5 items in a column. Use NSCollectionLayoutGroup.vertical instead of NSCollectionLayoutGroup.horizontal and insert 5 into the count.
Result
From iOS 13, we can implement very complicated ui layout very easily by using CompositionalLayout. You can also see many variety of layouts, check here.