SshConfig
The SshConfig makes it quick and easy to load, parse, and decode/encode the SSH configs. It also helps to resolve the properties by hostname and use them safely in your apps (thanks for Optional and static types in Swift).
Features
- Parsing a SSH config;
- Encode/Decode your config in JSON or text format;
- Resolve the SSH properties for a host by its alias;
- The static type checking SSH properties (yeah...If, in the beginning, I knew that there would be almost 100 properties, I would not begin to describe them!).
Usage
Let's try to load, parse and decode an SSH config file and look at a base scenario of how to work with it.
~/.ssh/config file content:
Host gitlab.com github.com
PreferredAuthentications publickey
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
User xxlabaza
Host my*
User admin
Port 2021
Host *
SetEnv POPA=3000
Code example:
import SshConfig
let config = try! ssh.Config.load(path: "~/.ssh/config")
let github = config.resolve(for: "github.com")
assert(github.preferredAuthentications == [.publickey])
assert(github.identityFile == ["~/.ssh/id_rsa"])
assert(github.user == "xxlabaza")
assert(github.setEnv == ["POPA": "3000"]) // from 'Host *'
assert(github.port == 22) // the default one
// github.com and gitlab.com resolve the same properties set
assert(github == config.resolve(for: "gitlab.com"))
let myserver = config.resolve(for: "myserver")
assert(myserver.user == "admin")
assert(myserver.port == 2021)
assert(myserver.setEnv == ["POPA": "3000"]) // from 'Host *'
let backend = config.resolve(for: "backend")
assert(backend.user == nil) // the default one
assert(backend.port == 22) // the default one
assert(backend.setEnv == ["POPA": "3000"]) // from 'Host *'
The same ssh.Config instance can be constructed programmatically, like this:
NOTE: I use variadic list of closures for setting needed properties for
ssh.Propertiesinstance, which creates inside thessh.Hostinitializer. I found that approach more similar to the original ssh config file format, plus you can ignore thessh.Properties's fields order.
import SshConfig
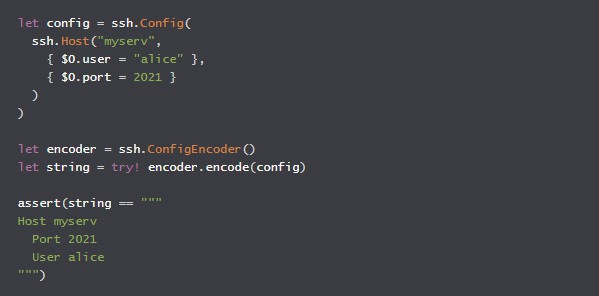
let config = ssh.Config(
ssh.Host("gitlab.com github.com",
{ $0.preferredAuthentications = [.publickey] },
{ $0.identityFile = ["~/.ssh/id_rsa"] },
{ $0.user = "xxlabaza" }
),
ssh.Host("my*",
{ $0.user = "admin" },
{ $0.port = 2021 }
),
ssh.Host("*",
{ $0.setEnv = ["POPA": "3000"] }
)
)
...
More code samples and examples are available in the website and in the tests (especially in UsageExample.swift file).
Installation
Requirements
Swift 5.1+
| iOS | watchOS | tvOS | macOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13+ | 6+ | 13+ | 10.15+ |
Swift Package Manager
NOTE: the instructions below are for using
SwiftPMwithout theXcode UI. It's the easiest to go to your Project Settings -> Swift Packages and add SshConfig from there.
Swift Package Manager - is the recommended installation method. All you need is to add the following as a dependency to your Package.swift file:
.package(url: "https://github.com/xxlabaza/SshConfig.git", from: "1.0.1"),
So, your Package.swift may look like below:
// swift-tools-version:5.1
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "MyPackage",
platforms: [ // The SshConfig requires the versions below as a minimum.
.iOS(.v13),
.watchOS(.v6),
.tvOS(.v13),
.macOS(.v10_15),
],
products: [
.library(name: "MyPackage", targets: ["MyPackage"]),
],
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/xxlabaza/SshConfig.git", from: "1.0.1"),
],
targets: [
.target(name: "MyPackage", dependencies: ["SshConfig"])
]
)
And then import wherever needed:
import SshConfig
CocoaPods
CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Cocoa projects. For usage and installation instructions, visit their website. To integrate SshConfig into your Xcode project using CocoaPods, specify it in your Podfile:
pod 'SshConfig'
Eventually, your Podfile should look like this one:
# The SshConfig requires the versions below as a minimum.
# platform :ios, '13.0'
platform :osx, '10.15'
# platform :tvos, '13.0'
# platform :watchos, '6.0'
target 'MyApp' do
use_frameworks!
pod 'SshConfig'
end
And then run:
pod install
After installing the cocoapod into your project import SshConfig with:
import SshConfig