Synopsis
YMTreeMap is a high performance treemap layout engine for iOS and macOS, written in Swift.
The input to YMTreeMap is a list of arbitrary numbers, and the output will be a list of layout rectangles representing those numbers graphically. The order of the layout rectangles will match the original input order, so you should sort the input numbers the way that you want your treemap to be ordered. Finally, the size of the layout rectangles will represent the relative weighting of the ordinal input number that it cooresponds to.
YMTreeMap uses the "squarified" layout treemap algorithm. Squarified optimizes for low aspect ratios: meaning it generates rectangles that are as square as possible given a reasonable effort. While not perfectly optimal, the algorithm get pretty close while maintaining high-performance.
The output rectangles can easily be used to render the shapes using whatever rendering system you prefer:
- Using CoreGraphics (in drawRect, etc)
- Using OpenGL
- Using a custom UICollectionView layout
Usage
Basic sample of how to draw a small heat map using random colors in Swift and Objective-C.
Swift
var randomColor: UIColor {
return UIColor(red: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(255) % 255) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(255) % 255) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(arc4random_uniform(255) % 255) / 255.0,
alpha: 1)
}
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let values = [ 445, 203, 110, 105, 95, 65, 33, 21, 10 ].sorted()
// These two lines are actual YMTreeMap usage!
let treeMap = YMTreeMap(withValues: values)
let treeMapRects = treeMap.tessellate(inRect: self.bounds)
let context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()
treeMapRects.forEach { (treeMapRect) in
randomColor.setFill()
context?.fill(treeMapRect)
}
}
Objective-C
#define RANDOM_COLOR [UIColor colorWithRed:(rand() % 255)/255.0 green:(rand() % 255)/255.0 blue:(rand() % 255)/255.0 alpha:1.0]
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
NSArray<NSNumber *> *values = @[ @445, @203, @110, @105, @95, @65, @33, @21, @10 ];
// These two lines are actual YMTreeMap usage!
YMTreeMap *tm = [[YMTreeMap alloc] initWithValues:values];
NSArray<NSValue *> *treeMapRects = [tm tessellateInRect:rect];
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
for (NSValue *rectVal in treeMapRects) {
[RANDOM_COLOR setFill];
CGContextFillRect(context, rectVal.CGRectValue);
}
}
Examples
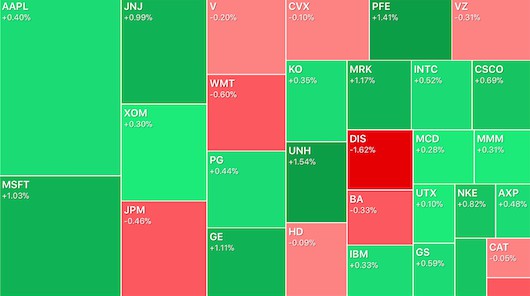
Here are examples of 30-item and 1000-item sorted treemaps in a verical-orientation.


Performance
Tests performed on-device after 3 seconds of idle time, in release configuration. All tests use the same input values, which were sorted lists of large integers.
Even with heat maps with up to 1,000 items, layout time is well controlled at 3.7ms. This should
enable use within a scrolling table view.
Pure Swift
iPhone 7 Plus
- [30 items ] Performed 1000 iterations in 114.331625ms; 8.746486/ms; 0.114332ms each
- [1000 items] Performed 1000 iterations in 3743.449875ms; 0.267133/ms; 3.743450ms each
Objective-C bridging into Swift
iPhone 7 Plus
- [30 items ] Performed 1000 iterations in 132.439167ms; 7.550636/ms; 0.132439ms each
- [1000 items] Performed 1000 iterations in 4493.055292ms; 0.222566/ms; 4.493055ms each
Example
To run the example project, clone the repo, and run pod install from the Example directory first.
Requirements
Installation
YMTreeMap is available through CocoaPods. To install
it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod 'YMTreeMap'
Further Reading
Various papers on treemapping layout algorithms and usability that helped influence this project. A copy of each paper is in the Research folder.
Squarified Treemaps - Mark Bruls, Kees Huizing, Jarke J. van Wijk
Ordered Treemap Layouts - Ben Shneiderman, Martin Wattenberg
Ordered and Quantum Treemaps: Making Effective Use of 2D Space to Display Hierarchies - Benjamin B. Bederson, Ben Shneiderman, Martin Wattenberg
Treemaps for space-constrained visualization of hierarchies - Ben Shneiderman
Animated Exploration of Dynamic Graphs with Radial Layout - Ka-Ping Yee, Danyel Fisher, Rachna Dhamija, Marti Hearst
Author
Adam Kaplan, [email protected]
License
YMTreeMap is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.