Localize
Localize is a framework written in swift to help you localize and pluralize your projects. It supports both storyboards and strings.

Features
- [x] Storyboard with IBInspectable
- [x] Pluralize and localize your keys
- [x] Keep the File.strings files your app already uses
- [x] Support Apple strings and JSON Files
- [x] Change your app language without changing device language
- [x] Localize your Storyboards without extra files or/and ids
Requirements
- iOS 9.0+
- Xcode 8.0+
- Swift 3.0+
Installation
CocoaPods
CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Cocoa projects. You can install it with the following command:
gem install cocoapods
CocoaPods 1.1.0+ is required to build Localize 1.+.
To integrate Localize into your Xcode project using CocoaPods, specify it in your Podfile:
source 'https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git'
platform :ios, '9.0'
use_frameworks!
target '<Your Target Name>' do
pod 'Localize' , '~> 2.3.0'
end
# If you are using Swift 4.x
# target '<Your Target Name>' do
# pod 'Localize' , '~> 2.1.0'
# end
Then, run the following command:
pod install
Carthage
Carthage is a decentralized dependency manager that builds your dependencies and provides you with binary frameworks.
You can install Carthage with Homebrew using the following command:
brew update
brew install carthage
To integrate Localize into your Xcode project using Carthage, specify it in your Cartfile:
github "andresilvagomez/Localize"
Run carthage update to build the framework and drag the built Localize.framework into your Xcode project.
Swift Package Manager
The Swift Package Manager is a tool for automating the distribution of Swift code and is integrated into the swift compiler.
Once you have your Swift package set up, adding Localize as a dependency is as easy as adding it to the dependencies value of your Package.swift.
dependencies: [
.Package(url: "https://github.com/andresilvagomez/Localize.git")
]
Usage
Add .localize() for any String if you want localize.
You don't need import anything in your code, Localize uses extensions to localize your Strings.
textLabel.text = "hello.world".localize()
// Or
textLabel.text = "hello.world".localized
You can decide if you want use JSON or Apple Strings, we support both, if you decide to use JSON please follow these instructions.
Create JSON file
Please create a JSON file in your code with this rule:
{your file name}-{your lang code}.json
For example
- lang-en.json
- lang-es.json
- lang-fr.json
Example JSON File
{
"hello" : {
"world" : "Hello world!",
"name" : "Hello %!"
},
"values" : "Hello % we are %, see you soon",
"username" : "My username is :username",
"navigation.title" : ""
}
Create String file
If you decide use Apple strings, please follow Apple Localization Guide to create strings file.
String file example
"hello.world" = "Hello world!";
"name" = "Hello %";
"values" = "Hello everyone my name is % and I'm %, see you soon";
"username" = "My username is :username";
"level.one.two.three" = "This is a multilevel key";
"the.same.lavel" = "This is a localized in the same level";
"enlish" = "This key only exist in english file.";
Whatever way you choose to, use that methods.
Localize strings
print( "hello.world".localize() )
// Hello world!
// Also you can use
print( "hello.world".localized )
Localize strings, replacing text
Localize use % identifier to replace the text
print( "hello.name".localize(value: "everyone") )
// Hello everyone!
Localize strings, replacing many texts
Localize use % identifier to replace the text
print( "values".localize(values: "everyone", "Software Developer") )
// Hello everyone we are Software Developer, see you soon
Localize strings, replacing dictionary values
Localize use :yourid to search your id in JSON File
print( "username".localize(dictionary: ["username": "Localize"]) )
// My username is Localize
Localize strings, using other files
If you decide use different files use methods with tableName in the end of each method, for example.
print( "hello.world".localize(tableName: "Other") )
print( "hello.name".localize(value: "everyone", tableName: "Errors") )
print( "values".localize(values: "everyone", "Software Developer", tableName: "YourFileName") )
print( "username".localize(dictionary: ["username": "Localize"], tableName: "YourFileName") )
We are amazing with storyboards
You don't need to import anything in your code, Localize uses extensions to localize your UIView components
To prevent auto localization for some controls you created in storyboard can set Auto Localize to Off

- lang-en.json
{
"navigation" : {
"title" : "Localize"
},
"app" : {
"label" : "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. Aenean massa. Cum sociis natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. Donec quam felis, ultricies nec, pellentesque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim. Donec pede justo, fringilla vel, aliquet nec, vulputate eget, arcu. In enim justo, rhoncus ut, imperdiet a, venenatis vitae, justo. Nullam dictum felis eu pede mollis pretium.",
"textfield" : "Write some here."
}
}
You can use extensions for
UIBarButtonItemUIButtonUILabelUINavigationItemUISearchBarUISegmentedControlUITabBarItemUITextFieldUITextView
Updating language
When you change a language, automatically all views update your content to new language
Localize.update(language: "fr")
To make this work with strings, you need to implement a notification
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(localize), name: NSNotification.Name(localizeChangeNotification), object: nil)
}
public func localize() {
yourLabel.text = "app.names".localize(values: "mark", "henrry", "peater")
otherLabel.text = "app.username".localize(value: "Your username")
}
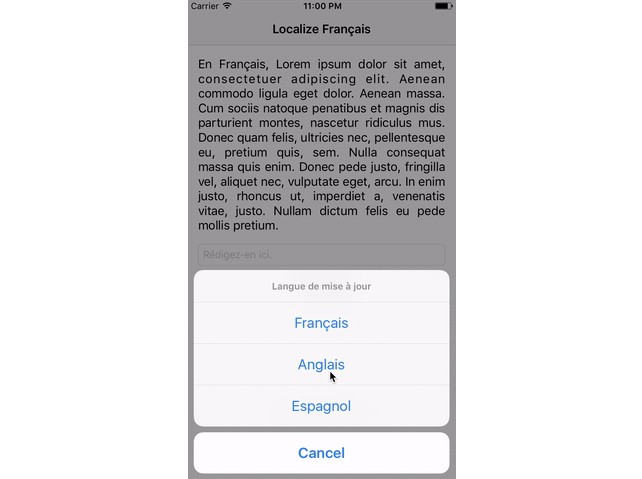
Implementing internal acction to change a language
@IBAction func updateLanguage(_ sender: Any) {
let actionSheet = UIAlertController(title: nil, message: "app.update.language".localize(), preferredStyle: UIAlertControllerStyle.actionSheet)
for language in Localize.availableLanguages {
let displayName = Localize.displayNameForLanguage(language)
let languageAction = UIAlertAction(title: displayName, style: .default, handler: {
(alert: UIAlertAction!) -> Void in
Localize.update(language: language)
})
actionSheet.addAction(languageAction)
}
let cancelAction = UIAlertAction(title: "Cancel", style: UIAlertActionStyle.cancel, handler: {
(alert: UIAlertAction) -> Void in
})
actionSheet.addAction(cancelAction)
self.present(actionSheet, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
Config
This not is necesary, only if you need different results.
// AppDelegate.swift
import Localize
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
let localize = Localize.shared
// Set your localize provider.
localize.update(provider: .json)
// Set your file name
localize.update(fileName: "lang")
// Set your default language.
localize.update(defaultLanguage: "fr")
// If you want change a user language, different to default in phone use thimethod.
localize.update(language: "en")
// If you want remove storaged language use
localize.resetLanguage()
// The used language
print(localize.currentLanguage)
// List of available language
print(localize.availableLanguages)
// Or you can use static methods for all
Localize.update(fileName: "lang")
Localize.update(defaultLanguage: "fr")
Localize.update(language: "en-DE")
return true
}
Pluralize
print( "people".pluralize(value: 0) )
// there are no people
print( "people".pluralize(value: 1) )
// only one person
print( "people".pluralize(value: 2) )
// two people
print( "people".pluralize(value: 27) )
// many people
print( "people".pluralize(value: 103) )
// hundreds of people
print( "people".pluralize(value: 1010) )
// thousand of people
print( "people".pluralize(value: 1000000) )
// millions of people
how you need compose your file.
// Json file
{
"people": {
"zero": "there are no people",
"one": "only one person",
"two": "two people",
"many": "many people",
"hundreds": "hundreds of people",
"thousand": "thousand of people",
"millions": "millions of people",
"other": "not defined people"
}
}
# string file
"people.zero" = "there are no people";
"people.one" = "only one person";
"people.two" = "two people";
"people.many" = "many people";
"people.hundreds" = "hundreds of people";
"people.thousand" = "thousand of people";
"people.millions" = "millions of people";
"people.other" = "not defined people";
but also you can show your value
print( "people".pluralize(value: 1) )
/// 1 Person
in your file
// JSON
{
"people": {
"one": "% Person",
...
}
}
// Strings
"people.one" = "% Person";
Notes for your AppStore release
To make all languages you have localized your app for visible on the AppStore, you must add a language in the project's settings.
- For that, click on your project name in the left side bar.
- Then, choose project, instead of a target.
- At the bottom, under Localizations, press the + button & select a language you want to add
- On prompt, uncheck all files Xcode wants to add localization for, but keep a single one, that you won't actually localize, such as your launch screen for instance.
- if you need to localize all your files, I suggest adding a placeholder storyboard file that you'll then add to localization
- Done! (You don't actually have to localize the placehodler file.) The AppStore will now show the new language in localizations for your app.
Credits
Special thanks to Benjamin Erhart
License
Localize is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.