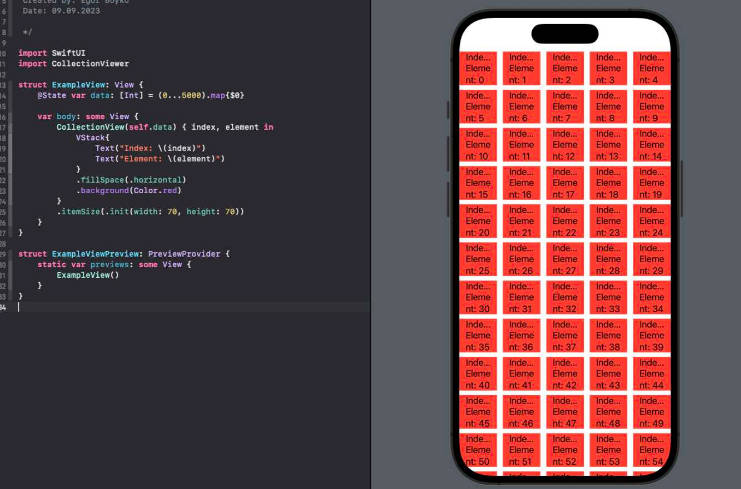
CollectionViewer
The package wraps the UICollectionView, providing a convenient interaction with SwiftUI.
Key features:
- Reactive connection with incoming data. You don’t have to worry about updating the cells, just change the incoming array.
- Automatic calculation of the size of displayed views.
- Data buffering – to improve performance
- Ability to update content with a native gesture
Designed to display static content (lists, tiles, etc.) that will not change size after display.
Package Goals
- The need for an analogue of the LazyVGrid with better performance and correct memory release on iOS 15 and below.
- Update gesture support on iOS 14
Warning
The package is in beta stage. It may and most likely contains errors. Use with caution.
Examples of using
Fully automatic use
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.background(Color.red)
}
}
}

Define columns
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(1)
}
}

struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(2)
}
}

Fill empty space with a modifier
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(1)
}
}

struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(2)
}
}

Manage sizes
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...5000).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.background(Color.red)
}
.itemSize(.init(width: 70, height: 70))
}
}

Update your incoming data
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...10).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.background(Color.red)
.onAppear{
if index == 5 {
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 1){
data.append(
contentsOf: (11...20).map{$0}
)
}
}
}
}
.itemSize(.init(width: 70, height: 70))
}
}

Don’t worry about the height
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...10).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
let height: CGFloat? = {
if index % 2 == 0 {
return 150
} else if index % 3 == 0 {
return 200
} else {
return nil
}
}()
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.frame(height: height)
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(1)
}
}

struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...10).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
let padding: CGFloat = {
if index % 2 == 0 {
return 20
} else if index % 3 == 0 {
return 40
} else {
return 60
}
}()
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
.padding(.bottom, padding)
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.padding(.vertical, 5)
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(1)
}
}

Update your data
struct ExampleView: View {
@State var data: [Int] = (0...10).map{$0}
var body: some View {
CollectionView(self.data) { index, element in
VStack{
Text("Index: \(index)")
Text("Element: \(element)")
}
.fillSpace(.horizontal)
.background(Color.red)
}
.gridColumns(1)
.refreshAction { completed in
self.data = []
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 1){
self.data = (20...33).map{$0}
completed()
}
}
.ignoresSafeArea()
}
}

Features of use
To achieve better performance, the package does not use constraints and the size is calculated based on the contents of the view. The data passes through the buffer and after calculations, the dimensions are saved for later reuse. Disable size caching if your content may change size after updating (then you can turn it back on)

In addition to sizes, representations are also not recalculated and are saved for further reuse. Do not update the data source at once, otherwise you will end up with old views. Use asynchronous operations for updates.