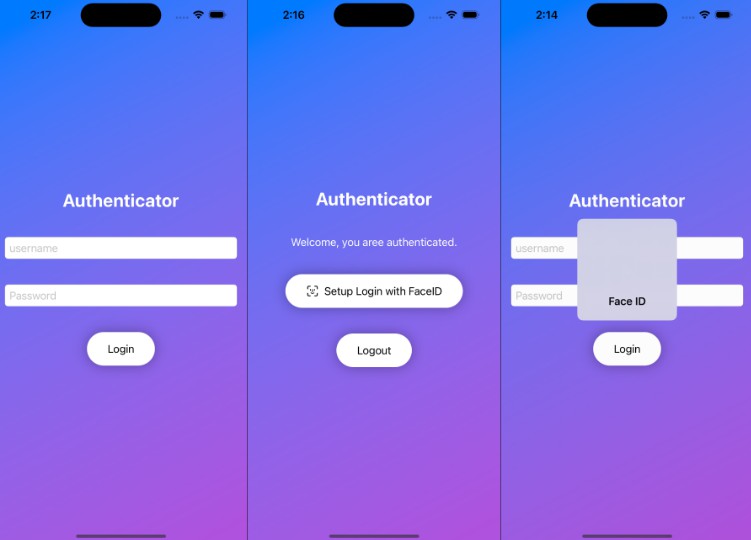
Authentication with FaceID and TouchID
The following demo shows how to use FaceID (or TouchID) to authenticate a user account on iOS 15/16.
There are five steps required to authenticate a user with FaceID:
- Import the
LocalAuthenticationframework into your code:import LocalAuthentication - Set the Privacy – Face ID Usage Description in your app’s Info.plist or the target’s Info settings
- Create a local authentication
contextinstance. This provides the interface between your app and device’s Secure Enclave:
// If you don't create a strong ref to LAContext() and reuse it you get weird runtime errors
private var context = LAContext()
- Use the local authentication context’s
canEvaluatePolicy(_:error:)method to check that you can actually use FaceID or TouchID. For example, the device might not support it, or the user may not have enabled it:
// Is Biometric security supported?
guard context.canEvaluatePolicy(LAPolicy.deviceOwnerAuthenticationWithBiometrics, error: nil) else {
print("FaceID or TouchID not supported")
result(.failure(.notSupported))
return
}
- Call the call the local authentication context’s
evaluatePolicy(_:localizedReason:reply:)method to authenticate the user:
// Use FaceID/TouchID to authenticate the user
context.evaluatePolicy(LAPolicy.deviceOwnerAuthenticationWithBiometrics, localizedReason: "Authentication required") { success, error in
guard success else {
print("Error authenticating: \(error?.localizedDescription ?? "unknown error")")
return
}
print("Successfully authenticated")
}
Here we encapsulate everything required in a BioSecurity class:
//
// BioSecurity.swift
//
// Created by Russell Archer on 03/08/2022.
//
import LocalAuthentication
enum BioAuthenticationError: Error {
case notSupported, failed
}
class BioSecurity {
private var context = LAContext()
func isSupported() -> Bool {
switch typeSupported() {
case .faceID: return true
case .touchID: return true
default: return false
}
}
func typeSupported() -> LABiometryType {
// LAContext().biometryType is always none until you call canEvaluatePolicy(_:error:)
guard context.canEvaluatePolicy(LAPolicy.deviceOwnerAuthenticationWithBiometrics, error: nil) else {
return .none
}
return context.biometryType
}
func typeSupportedDescription() -> String {
switch typeSupported() {
case .faceID: return "FaceID"
case .touchID: return "TouchID"
default: return "None"
}
}
func authenticate(result: @escaping (Result<String, BioAuthenticationError>) -> Void) {
// Get a fresh context for each login. If you use the same context on multiple attempts
// then a previously successful authentication causes the next policy evaluation to succeed
// without testing biometry again
context = LAContext()
// Is Biometric security supported?
guard context.canEvaluatePolicy(LAPolicy.deviceOwnerAuthenticationWithBiometrics, error: nil) else {
print("Biometric security not supported")
result(.failure(.notSupported))
return
}
let bioType = typeSupportedDescription()
// Use Biometry to authenticate the user
context.evaluatePolicy(LAPolicy.deviceOwnerAuthenticationWithBiometrics, localizedReason: "Authentication required") { success, error in
// Note: Return all results on the main thread
guard success else {
Task { @MainActor in
print("Error authenticating: \(error?.localizedDescription ?? "unknown error")")
result(.failure(BioAuthenticationError.failed))
}
return
}
Task { @MainActor in
result(.success(bioType))
}
}
}
}
And a minimal SwiftUI view that uses our BioSecurity class looks as follows:
//
// ContentView.swift
//
// Created by Russell Archer on 03/08/2022.
//
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var isSupported = false
@State var authenticated : Bool?
var bioSec = BioSecurity()
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button(action: {
bioSec.authenticate() { result in
switch result {
case .failure(_): authenticated = false
case .success(_): authenticated = true
}
}
}, label: {
Label("Authenticate", systemImage: "person.badge.key.fill")
})
.padding()
.disabled(!isSupported)
Text("Biometric authentication \(isSupported ? "" : "not") supported")
.padding()
.font(.footnote)
if let auth = authenticated {
Text(auth ? "Authenticated ?" : "Authentication failed ☹️")
.padding()
.font(.largeTitle)
.foregroundColor(auth ? .green : .red)
}
Spacer()
}
.task {
isSupported = bioSec.isSupported()
}
}
}
The UI consists of just a single button that allows the user to authenticate (if it’s supported).