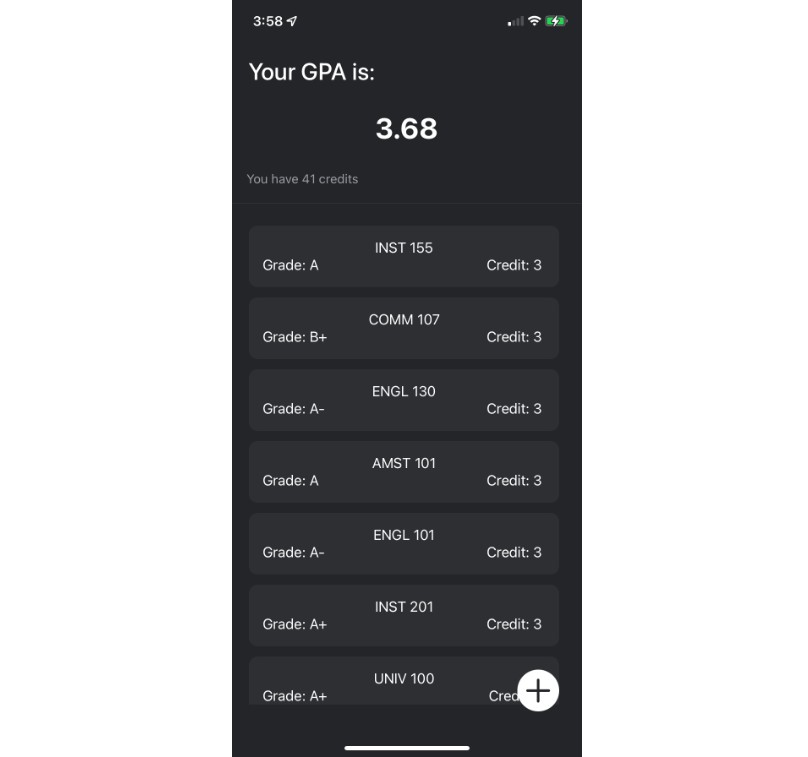
SwiftTabler
A multi-platform SwiftUI component for displaying (and interacting with) tabular data.
Available as an open source library to be incorporated in SwiftUI apps.
SwiftTabular is part of the OpenAlloc family of open source Swift software tools.
| macOS | iOS |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Features
- Convenient display of tabular data from a
RandomAccessCollectionor Core Data source - Presently targeting macOS v11+ and iOS v14+**
- Supporting bound and unbound arrays, and Core Data too
- With bound data, add inline controls to interactively change (and mutate) your data model
- Optional sort-by-column support, with concise syntax
- Optional support for colored rows, with selection overlay
- No View type erasure (i.e., use of
AnyView), which can impact scalability and performance - No external dependencies!
For List-based tables:
- Optional moving of rows through drag and drop
- Support for no-select, single-select, and multi-select
For ScrollView/LazyVStack-based tables:
- Support for no-select and single-select (possibily multi-select in future)
For ScrollView/LazyVGrid-based tables:
- Likely the most scalable and efficient, but least flexible
On macOS:
- Hovering highlight, indicating which row the mouse is over
** Other platforms like macCatalyst, iPad on Mac, watchOS, tvOS, etc. are poorly supported, if at all. Please contribute to improve support!
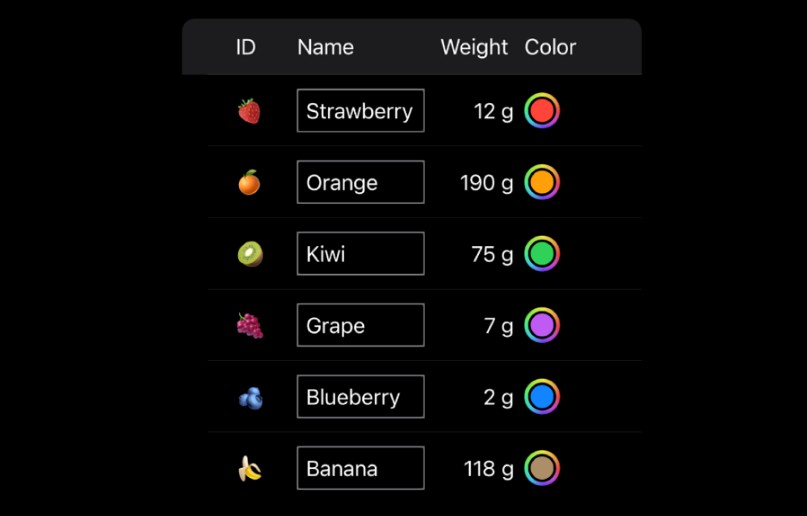
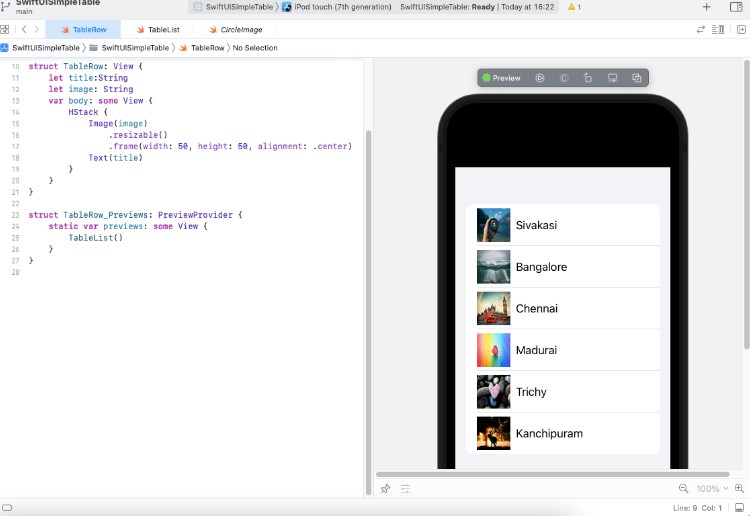
Tabler Example
The basic example below shows the basic display of tabular data using TablerList, which is for the display of unbound data without any selection capability.
import SwiftUI
import Tabler
struct Fruit: Identifiable {
var id: String
var name: String
var weight: Double
var color: Color
}
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var fruits: [Fruit] = [
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Banana", weight: 118, color: .brown),
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Strawberry", weight: 12, color: .red),
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Orange", weight: 190, color: .orange),
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Kiwi", weight: 75, color: .green),
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Grape", weight: 7, color: .purple),
Fruit(id: "?", name: "Blueberry", weight: 2, color: .blue),
]
private var gridItems: [GridItem] = [
GridItem(.flexible(minimum: 35, maximum: 40), alignment: .leading),
GridItem(.flexible(minimum: 100), alignment: .leading),
GridItem(.flexible(minimum: 40, maximum: 80), alignment: .trailing),
GridItem(.flexible(minimum: 35, maximum: 50), alignment: .leading),
]
@ViewBuilder
private func header(_ ctx: TablerSortContext<Fruit>) -> some View {
Text("ID")
Text("Name")
Text("Weight")
Text("Color")
}
@ViewBuilder
private func row(_ element: Fruit) -> some View {
Text(element.id)
Text(element.name).foregroundColor(element.color)
Text(String(format: "%.0f g", element.weight))
Image(systemName: "rectangle.fill").foregroundColor(element.color)
}
var body: some View {
TablerList(config,
headerContent: header,
rowContent: row,
results: fruits)
.padding()
}
private var config: TablerListConfig<Fruit> {
TablerListConfig<Fruit>(gridItems: gridItems)
}
}
Tables
You can choose from any of ten (10) variants, which break down along the following lines:
- List-based, ScrollView/LazyVStack-based, and ScrollView/LazyVGrid-based
- Selection types offered: none, single-select, and multi-select, depending on base
- Unbound elements in row view, where you’re presenting table rows read-only*
- Bound elements in row view, where you’re presenting tables rows that can be updated directly (see Bound section below)
| Base | Selection of rows | Element wrapping | View name | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| List | No Select | (none) | TablerList | |
| List | No Select | Binding<Element> | TablerListB | |
| List | Single-select | (none) | TablerList1 | |
| List | Single-select | Binding<Element> | TablerList1B | |
| List | Multi-select | (none) | TablerListM | |
| List | Multi-select | Binding<Element> | TablerListMB | |
| Stack | No Select | (none) | TablerStack | |
| Stack | No Select | Binding<Element> | TablerStackB | |
| Stack | Single-select | (none) | TablerStack1 | |
| Stack | Single-select | Binding<Element> | TablerStack1B | |
| Grid | No Select | (none) | TablerGrid | Experimental. Needs bound version, select, etc. |
* ‘unbound’ variants can be used with Core Data (where values are bound by alternative means)
Column Sorting
Column sorting is available through tablerSort view function.
From the demo app, an example of using the sort capability:
@ViewBuilder
private func header(_ ctx: TablerSortContext<Fruit>) -> some View {
Text("ID \(Sort.indicator(ctx, \.id))")
.onTapGesture { tablerSort(ctx, &fruits, \.id) { $0.id < $1.id } }
Text("Name \(Sort.indicator(ctx, \.name))")
.onTapGesture { tablerSort(ctx, &fruits, \.name) { $0.name < $1.name } }
Text("Weight \(Sort.indicator(ctx, \.weight))")
.onTapGesture { tablerSort(ctx, &fruits, \.weight) { $0.weight < $1.weight } }
Text("Color")
}
When the user clicks on a header column for the first time, it is sorted in ascending order, with an up-arrow “▲” indicator. If clicked a successive time, a descending sort is executed, with a down-arrow “▼” indicator.
For sorting with Core Data, see the TablerCoreDemo app.
Bound data
| macOS | iOS |
|---|---|
 |
 |
When used with ‘bound’ variants (e.g., TablerListB), the data can be modified directly, mutating your data source. From the demo:
@ViewBuilder
private func brow(_ element: Binding<Fruit>) -> some View {
Text(element.wrappedValue.id)
TextField("Name", text: element.name)
.textFieldStyle(.roundedBorder)
Text(String(format: "%.0f g", element.wrappedValue.weight))
ColorPicker("Color", selection: element.color)
.labelsHidden()
}
Colored Rows
| macOS | iOS |
|---|---|
 |
 |
The demo app (link below) shows how colored rows are implemented.
Because the normal selection is obscured with colored rows, the ability to use a ‘selection overlay’ is provided. An example is available in the demo.
Disable Header
The demo app shows how to toggle the display of the header, where a header may not be desired.
Moving Rows
TODO add details here, with example of move action handler.
See Also
- TablerDemo – the demonstration app for this library, for
RandomAccessCollectiondata sources - TablerCoreDemo – the demonstration app for this library, for Core Data sources
Swift open-source libraries (by the same author):
- SwiftDetailer – multi-platform SwiftUI component for editing fielded data
- AllocData – standardized data formats for investing-focused apps and tools
- FINporter – library and command-line tool to transform various specialized finance-related formats to the standardized schema of AllocData
- SwiftCompactor – formatters for the concise display of Numbers, Currency, and Time Intervals
- SwiftModifiedDietz – A tool for calculating portfolio performance using the Modified Dietz method
- SwiftNiceScale – generate ‘nice’ numbers for label ticks over a range, such as for y-axis on a chart
- SwiftRegressor – a linear regression tool that’s flexible and easy to use
- SwiftSeriesResampler – transform a series of coordinate values into a new series with uniform intervals
- SwiftSimpleTree – a nested data structure that’s flexible and easy to use
And commercial apps using this library (by the same author):
- FlowAllocator – portfolio rebalancing tool for macOS
- FlowWorth – a new portfolio performance and valuation tracking tool for macOS
License
Copyright 2022 FlowAllocator LLC
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the “License”); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an “AS IS” BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome. You are encouraged to submit pull requests to fix bugs, improve documentation, or offer new features.
The pull request need not be a production-ready feature or fix. It can be a draft of proposed changes, or simply a test to show that expected behavior is buggy. Discussion on the pull request can proceed from there.