SwiftUI Snapping ScrollView
Add snapping behaviour to a SwiftUI ScrollView.
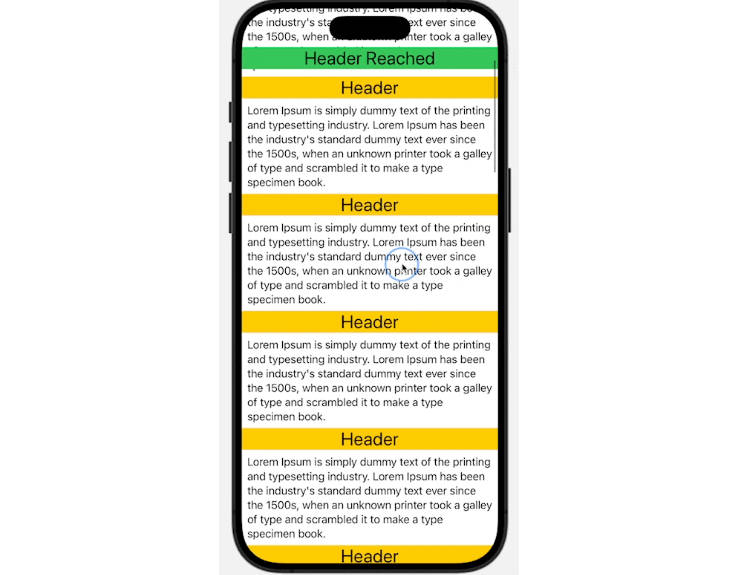
SnappingScrollView
A scrollable view that supports snapping.
Usage
SnappingScrollView(.vertical) {
//Header view
.snappingScrollAnchor(.bounds)
//Content views
}
Parameters
axis: The scroll view’s scrollable axis. The default axis is the vertical axis.decelerationRate: A floating-point value that determines the rate of deceleration after the user ends dragging. The default value for this parameter is.normal.showsIndicators: A Boolean value that indicates whether the scroll view displays the scrollable component of the content offset, in a way suitable for the platform. The default value for this parameter istrue.content: The view builder that creates the scrollable view.
snappingScrollAnchor
A function that sets the scroll snapping anchor rect for a view.
Avoid setting the scroll snapping anchor rect on a child of a lazy view, such as a LazyHGrid, LazyVGrid, LazyHStack or LazyVStack.
Parameters
source: The source of the anchor rect.
Advanced Usage
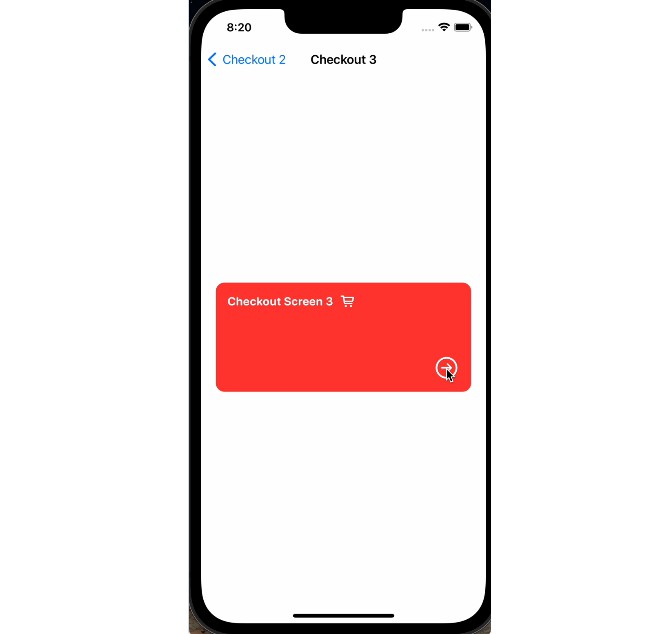
SnappingScrollView can provide paging behaviour when initialised with a decelerationRate of .fast. Add the pages to a stack view with spacing set to 0. Any desired spacing should be added as padding to the edge of each page view:
SnappingScrollView(.horizontal, decelerationRate: .fast) {
HStack(spacing: 0) {
ForEach(...) {
//Page view
.padding(.trailing)
.snappingScrollAnchor(.bounds)
}
}
}
snappingScrollAnchor should not be used on a child of a lazy view. Instead, use non-lazy parent views, and use onVisible to load data or update subviews when the view’s bounds move into the visible frame. Provide padding to increase the distance from the visible frame that the action is called.
Requirements
- iOS 13.0+
- Xcode 12.0+
Installation
- Install with Swift Package Manager.
- Import
SwiftUISnappingScrollViewto start using.
Contact
@ciaranrobrien on Twitter.