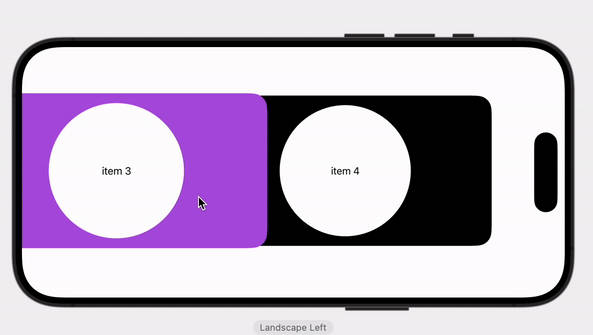
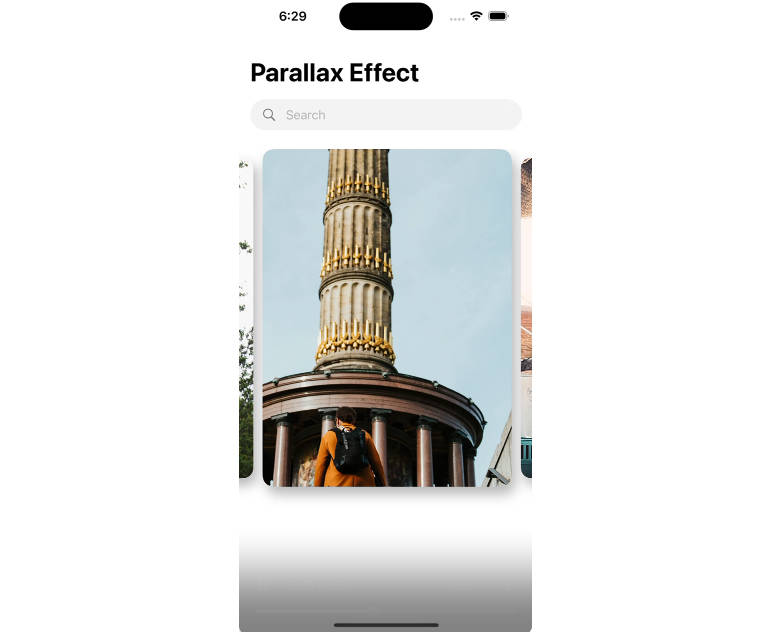
This framework lets you populate a carousel with an array of views. Pages can occupy the full width of the carousel or be inset slightly to show part of the adjacent pages. The carousel can be navigated by panning, swiping, or tapping on the page control.
Licensing
Y—Carousel is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
Documentation
Documentation is automatically generated from source code comments and rendered as a static website hosted via GitHub Pages at: https://yml-org.github.io/ycarousel-ios/
Usage
CarouselView
Simple use case
import YCarousel
final class ViewController: UIViewController {
private let carouselView: CarouselView = {
let page1 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial1"))
let page2 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial2"))
let page3 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial3"))
let carouselView = CarouselView(views: [page1, page2, page3])
return carouselView
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.addSubview(carouselView)
carouselView.constrainSize(width: 300, height: 300)
carouselView.constrainCenter()
}
}
Using a data source
import YCarousel
final class ViewController: UIViewController {
private let carouselView = CarouselView()
private let dataSource = CarouselViewProvider()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
carouselView.dataSource = dataSource
view.addSubview(carouselView)
carouselView.constrainSize(width: 300, height: 300)
carouselView.constrainCenter()
}
}
final class CarouselViewProvider {
private let imageNames = ["tutorial1", "tutorial2", "tutorial3"]
}
extension CarouselViewProvider: CarouselViewDataSource {
func carouselView(pageAt index: Int) -> UIView {
UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: imageNames[index]))
}
var numberOfPages: Int { imageNames.count }
}
CarouselViewController
Use case 1: pages as views
import YCarousel
let page1 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial1"))
let page2 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial2"))
let page3 = UIImageView(image: UIImage(named: "tutorial3"))
let pages = [page1, page2, page3]
let carouselViewController = CarouselViewController(views: pages)
present(carouselViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
Use case 2: pages as child view controllers
import YCarousel
let childVC1 = OnboardingViewController()
let childVC2 = OnboardingViewController()
let childVC3 = OnboardingViewController()
let childVCs = [childVC1, childVC2, childVC3]
let carouselViewController = CarouselViewController(viewControllers: childVCs)
present(carouselViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
Installation
You can add Y—Carousel to an Xcode project by adding it as a package dependency.
- From the File menu, select Add Packages…
- Enter “https://github.com/yml-org/ycarousel-ios” into the package repository URL text field
- Click Add Package
Contributing to Y—Carousel
Requirements
SwiftLint (linter)
brew install swiftlint
Jazzy (documentation)
sudo gem install jazzy
Setup
Clone the repo and open Package.swift in Xcode.
Versioning strategy
We utilize semantic versioning.
{major}.{minor}.{patch}
e.g.
1.0.5
Branching strategy
We utilize a simplified branching strategy for our frameworks.
- main (and development) branch is
main - both feature (and bugfix) branches branch off of
main - feature (and bugfix) branches are merged back into
mainas they are completed and approved. maingets tagged with an updated version # for each release
Branch naming conventions:
feature/{ticket-number}-{short-description}
bugfix/{ticket-number}-{short-description}
e.g.
feature/CM-44-button
bugfix/CM-236-textview-color
Pull Requests
Prior to submitting a pull request you should:
- Compile and ensure there are no warnings and no errors.
- Run all unit tests and confirm that everything passes.
- Check unit test coverage and confirm that all new / modified code is fully covered.
- Run
swiftlintfrom the command line and confirm that there are no violations. - Run
jazzyfrom the command line and confirm that you have 100% documentation coverage. - Consider using
git rebase -i HEAD~{commit-count}to squash your last {commit-count} commits together into functional chunks. - If HEAD of the parent branch (typically
main) has been updated since you created your branch, usegit rebase mainto rebase your branch.- Never merge the parent branch into your branch.
- Always rebase your branch off of the parent branch.
When submitting a pull request:
- Use the provided pull request template and populate the Introduction, Purpose, and Scope fields at a minimum.
- If you’re submitting before and after screenshots, movies, or GIF’s, enter them in a two-column table so that they can be viewed side-by-side.
When merging a pull request:
- Make sure the branch is rebased (not merged) off of the latest HEAD from the parent branch. This keeps our git history easy to read and understand.
- Make sure the branch is deleted upon merge (should be automatic).
Releasing new versions
- Tag the corresponding commit with the new version (e.g.
1.0.5) - Push the local tag to remote
Generating Documentation (via Jazzy)
You can generate your own local set of documentation directly from the source code using the following command from Terminal:
jazzy
This generates a set of documentation under /docs. The default configuration is set in the default config file .jazzy.yaml file.
To view additional documentation options type:
jazzy --help
A GitHub Action automatically runs each time a commit is pushed to main that runs Jazzy to generate the documentation for our GitHub page at: https://yml-org.github.io/ycarousel-ios/