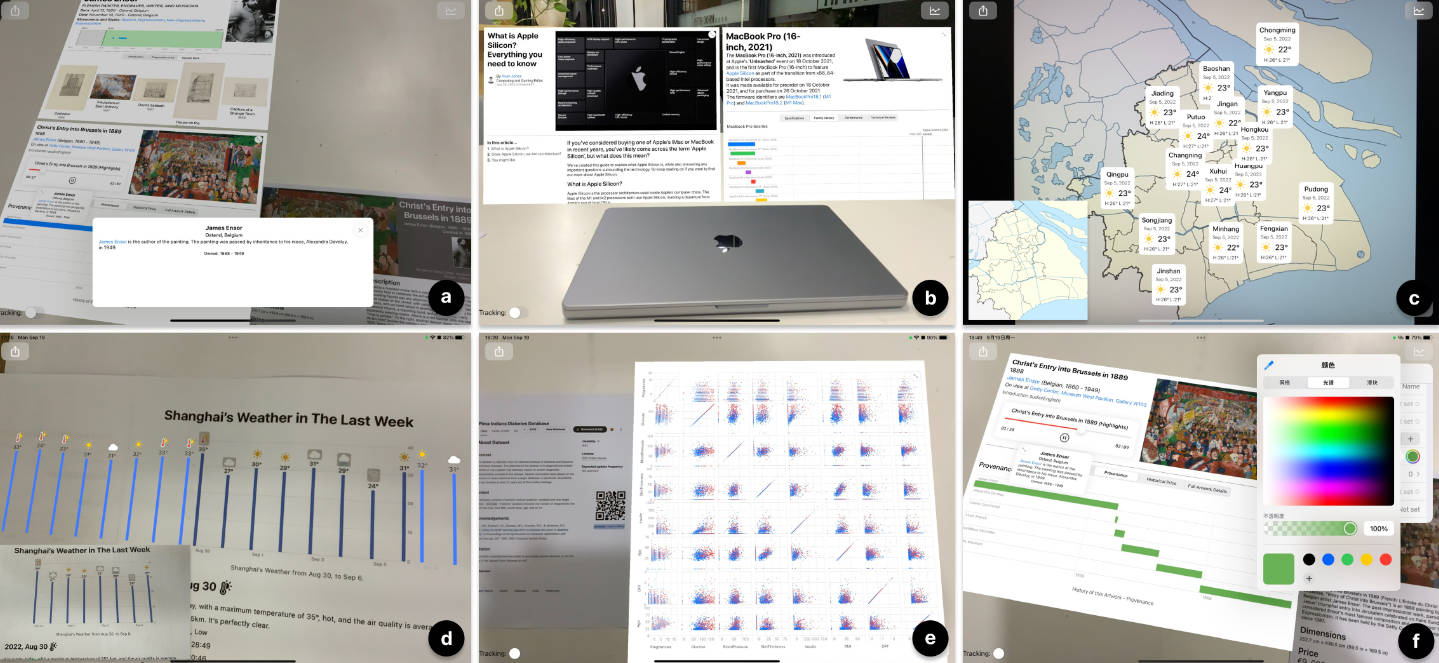
iARVis
iARVis is a proof-of-concept open-source toolkit for creating information and data visualization environment in augmented reality using declarative grammar (JSON) and its APIs. iARVis supports creating visualization widgets containing charts, rich text, images, videos, audios, etc. iARVis also supports advanced features such as hot-reload, automatic positioning, persistence and continuity, etc.
Build
-
Run
pod installin the root of the project(make sure you’ve installed cocoapods). -
Open
iARVis.xcworkspacewith Xcode.
Supported Platforms
iARVis only supports iOS now. We’ve made technical research that in what platforms can we implement our ideas. The idea of iARVis is general, which means it could be reimplemented in other platforms if they provide the same level of features.
Here is a comparison between suppoted features of ARCore (Android’s native AR engine) and ARKit (iOS’s native AR engine).
| Feature | ARCore | ARKit |
|---|---|---|
| Session | ✓ | ✓ |
| Device tracking | ✓ | ✓ |
| Camera | ✓ | ✓ |
| Plane detection | ✓ | ✓ |
| Image tracking | ✓ | ✓ |
| Object tracking | ✓ | |
| Face tracking | ✓ | ✓ |
| Body tracking | ✓ | |
| Point clouds | ✓ | ✓ |
| Raycasts | ✓ | ✓ |
| Anchors | ✓ | ✓ |
| Meshing | ✓ | |
| Environment probes | ✓ | ✓ |
| Occlusion | ✓ | ✓ |
| Participants | ✓ |
ARCore doesn’t support object tracking, which is critical to the automatic positioning feature. As a proof-of-concept toolkit, we choose iOS as our implementation platform.
Technical Architecture
iARVis is implemented on top of native technologies on iOS, for example, using ARKit as the AR engine and SwiftUI as the 2D content rendering engine. iARVis is responsible for parsing the specification, creating the visualization environment in AR, managing the interaction, persisting the environment, etc.
iARVis can accept a JSON specification, and use a parser to parse the specification to a configuration. iARVis can use the configuration to generate the widget configuration, use native frameworks such as SwiftUI, UIKit and Charts to render the widget and add interactions. iARVis is responsible for coordinating the rendering system and the augmented reality system. iARVis uses SceneKit to place rendered widgets in the 3D scene to implement the automaitc positioning feature. Hot-reload is implemented by periodically fetching the JSON specification and comparing the configuration. If the configuration is changed, iARVis will rerender the widget using new configuration.
Usage
Authoring
JSON
- Create a new JSON file and open with a preferred JSON editor, for example, Visual Studio Code
- Write a valid JSON specification
- We can use iARVis’s JSON schema to quickly check the grammar of the specification (currently under development)
- Deploy the JSON specification on a server (the most simple way is using GitHub’s repo as a specification hub)
- Open the JSON specification with the URL in iARVis’s client to validate the prototype. We can turn on the hot-reload feature to watch the change of the specification for quick validation.
For example, this is a valid JSON specification for a chart:
{
"dataSources": [
{
"label": "default",
"data": {
"model": [
"Medion Erazer Beast X25",
"Apple Macbook Pro 2021 16\" (10/32)",
"Medion Erazer e25",
"Apple Macbook Pro 2021 14\" (10/16)",
"Apple Macbook Pro 2021 14\" (8/14)",
"Apple MacBook Air 2020 M1 (8/8)",
"Apple MacBook Air 2020 M1 (8/7)",
"Dell XPS 15 9570",
"MSI Prestige 14 Evo A11M"
],
"CPU": [
"Ryzen 9 5900HX",
"M1 Max 10-core",
"Ryzen 5 5600H",
"M1 Pro 10-core",
"M1 Pro 8-core",
"M1",
"M1",
"Ci7-8750H",
"Ci7-1195G7"
],
"GPU": [
"GF RTX 3080",
"M1 Max 32-core",
"GF RTX 3050 Ti",
"M1 Pro 16-core",
"M1 Pro 14-core",
"M1 8-core",
"M1 7-core",
"GF GTX 1050 Ti Max-Q",
"Ci7-1195G7"
],
"score": [
22.686,
20.253,
10.634,
10.424,
9.272,
5.015,
4.518,
4.422,
3.885
]
}
}
],
"components": [
{
"type": "BarMark",
"config": {
"dataKey": "default",
"x": {
"field": "model"
},
"y": {
"field": "score"
},
"conditionalAnnotations": [
{
"field": "model",
"value": "Apple Macbook Pro 2021 16\" (10/32)",
"annotation": {
"position": "top",
"content": {
"text": {
"content": "Apple Macbook Pro 2021 16\" (10/32)",
"fontStyle": {
"size": 14,
"weight": "bold"
}
}
}
}
}
],
"foregroundStyleColorMap": [
{
"field": "model",
"value": "Apple Macbook Pro 2021 16\" (10/32)",
"color": "#FFA500"
}
]
}
},
],
"styleConfiguration": {
"maxWidth": 800,
"maxHeight": 450
},
"chartYScale": {
"includingZero": false
}
}
API
We can also directly create the configuration instead of writing a JSON specification using code.
Example:
let widgetComponent: ViewElementComponent = {
.vStack(elements: [
.hStack(elements: [
.vStack(elements: [
.text(content: "Christ's Entry into Brussels in 1889", fontStyle: ARVisFontStyle(size: 24, weight: .bold)),
.text(content: "1888", fontStyle: ARVisFontStyle(size: 20, weight: .medium)),
], alignment: .leading, spacing: 4),
.image(url: "..."),
], alignment: .top),
], alignment: .leading, spacing: 4)
}()
let widgetConfiguration = WidgetConfiguration(component: widgetComponent, relativeAnchorPoint: .top, relativePosition: .zero)
let trackingConfiguration: ImageTrackingConfiguration = .init(
imageURL: "...",
relationships: [
.init(widgetConfiguration: .init(component: .widgetComponent,
relativeAnchorPoint: .trailing,
relativePosition: SCNVector3(0.005, 0, 0))),
]
)
Client
A typical iARVis application uses QR Code (contains a URL points to a specification) scanning to open the visualization environment. We can also consider other ways to open the visualization environment, such as image recognition, object recognition, and NFC.
iARVis also supports iOS’s URL Scheme, which can be used to open a specification using urls like iARVis://openVisConfig?url=....
We can programatically set the configuration of iARVis in the client:
let viewController = ARKitViewController()
viewController.setVisualizationConfiguration(conf)
Components
Text
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case text(content: String, multilineTextAlignment: ARVisTextAlignment? = nil, fontStyle: ARVisFontStyle? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
JSON Example
{
"text": {
"content": "Alexandra Daveluy, who's James Ensor's niece, sold the painting to an Ostend casino proprietor named Gustave Nellens for $40,000.",
"fontStyle": {
"size": 14,
"weight": "regular"
}
}
}
Image
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case image(url: String, contentMode: ARVisContentMode = .fit, width: CGFloat? = nil, height: CGFloat? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
JSON Example
{
"image": {
"url": "https://www.theartstory.org/images20/works/ensor_james_1.jpg?1",
"contentMode": "fit",
"width": 200
}
}
Audio
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case audio(title: String? = nil, url: String, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
Video
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case video(url: String, width: CGFloat? = nil, height: CGFloat? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
SF Symbol
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case sfSymbol(name: String, size: CGFloat? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
HStack
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case hStack(elements: [ViewElementComponent], alignment: ARVisVerticalAlignment? = nil, spacing: CGFloat? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
VStack
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case vStack(elements: [ViewElementComponent], alignment: ARVisHorizontalAlignment? = nil, spacing: CGFloat? = nil, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
Grid
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case grid(rows: [ViewElementComponent], modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
case gridRow(rowElements: [ViewElementComponent], modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
Segmented Control
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case segmentedControl(items: [ARVisSegmentedControlItem], modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
struct ARVisSegmentedControlItem: Codable, Hashable {
var title: String
var component: ViewElementComponent
}
Divider
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case divider(opacity: CGFloat = 0.5, modifiers: [ViewElementComponentModifier]? = nil)
}
Spacer
Source
enum ViewElementComponent: Codable, Hashable {
case spacer
}
ARVisTextAlignment
Source
enum ARVisTextAlignment: String, Codable, Hashable {
case center
case leading
case trailing
}
ARVisFontStyle
Source
struct ARVisFontStyle: Codable, Equatable, Hashable {
let size: CGFloat
let weight: Weight?
let design: Design?
let color: ARVisColor?
}
extension ARVisFontStyle {
enum Weight: String, Codable, Equatable {
case black
case bold
case heavy
case light
case medium
case regular
case semibold
case thin
case ultraLight
}
}
extension ARVisFontStyle {
enum Design: String, Codable, Equatable {
case `default`
case monospaced
case rounded
case serif
}
}
ARVisContentMode
Source
enum ARVisContentMode: String, Codable, Hashable {
case fit
case fill
}
Widget Configuration
Source
class WidgetConfiguration: Codable, Hashable, ObservableObject {
var component: ViewElementComponent
var relativeAnchorPoint: WidgetAnchorPoint
var relativePosition: SCNVector3
var positionOffset: SCNVector3
var alignedToTarget: Bool
var isOpaque: Bool
var isScrollEnabled: Bool
var showExpandButton: Bool
var padding: [CGFloat]
var scale: CGFloat
var size: CGSize
// ...
}
enum WidgetAnchorPoint: String, Codable, Equatable, CaseIterable {
case auto
case center
case leading
case trailing
case top
case bottom
case cover
// Only for object tracking
case center0
case leading0
case trailing0
case top0
case bottom0
case center1
case leading1
case trailing1
case top1
case bottom1
case center2
case leading2
case trailing2
case top2
case bottom2
}
Image Tracking Configuration
Source
class ImageTrackingConfiguration: Codable, Equatable {
var imageURL: URL
var relationships: [WidgetImageRelationship]
}
class WidgetImageRelationship: Codable, Hashable {
var widgetConfiguration: WidgetConfiguration
}
Object Tracking Configuration
Source
class ObjectTrackingConfiguration: Codable, Equatable {
var objectURL: URL
var relationships: [WidgetObjectRelationship]
}
class WidgetObjectRelationship: Codable, Hashable {
var widgetConfiguration: WidgetConfiguration
}