ResizableSheet
ResizableSheeet is a half modal view library for SwiftUI.
You can easily implement a half modal view.
Target
- Swift5.5
- iOS14+
Installation
Only SwiftPM
Features
- 3 states are supported.
- hidden
- medium
- large
- The medium size is automatically calculated baesd on the content.
- You can update view for each state.
- ResizableSheet contains
ResizableScrollViewandTrackableScrollView.
TrackableScrollViewis a wrapper view ofUIScrollViewand the offset synchronizes with dragging of sheet.
ResizableScroolViewis a wrapper class ofTrackableScrollView, and - ResizableSheet can be shonw on another ResizableSheet.
Simple Example
To use ResizableSheet, follow these steps.
- Create
ResizableSheetCenterand embed it to your view in your root view likeRootView.
struct RootView: View {
let windowScene: UIWindowScene?
var resizableSheetCenter: ResizableSheetCenter? {
windowScene.flatMap(ResizableSheetCenter.resolve(for:))
}
var body: some View {
YOUR_VIEW
.environment(\.resizableSheetCenter, resizableSheetCenter)
}
}
- Prepare
ResizableSheetStatewith@State, and callresizableSheet.
You can customize the resizableSheet by chaining some methods.
struct SomeView: View {
@State var state: ResizableSheetState = .hidden
var body: some View {
Button("Show sheet") {
state = .medium
}
.resizableSheet($state) { builder in
builder.content { context in
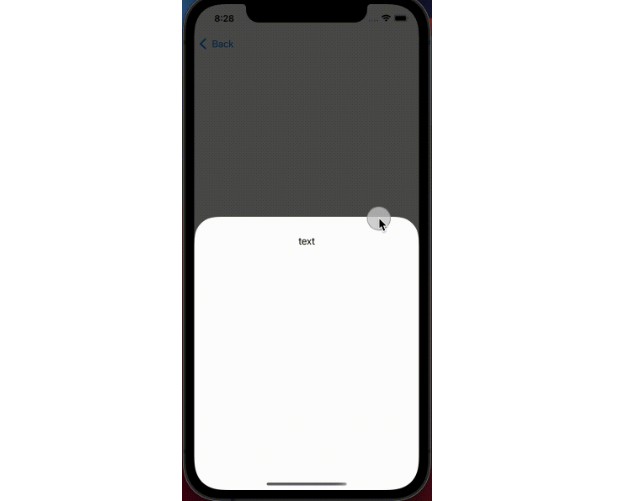
Text("text")
.padding()
}
}
}
}
That’s all!
You can show a half modal view by tapping the button “Show sheet”, and you can expand or remove the sheet by dragging it.
View structure
ResizableSheet has some view components.
You can control each view components based on current status.
ResizableSheet
└─ background
├─ outside
└─ sheet background
└─ content
Example
Complex Layout
You can update the view based on the current status.
The argument context has some informatios about the sheet, like state, view size, progress of dragging and diffY.
Based on the context, you can update the content.
Tips: Don’t forget to add .allowsHitTesting(false) to Color view. If you don’t add it, the dragging gesture is not recognized.
view.resizableSheet($state) { builder in
builder.content { context in
VStack {
Text(context.state == .hidden ? "hidden" :
context.state == .medium ? "medium" : "large"
)
Color.gray
.frame(height:
context.state == .medium ? max(0, context.diffY) :
context.state == .hidden ? 0 : nil
)
.opacity(context.state == .medium ? context.progress : 1.0 - abs(context.progress))
.allowsHitTesting(false)
Text("Buttom")
}
.padding()
}
}
Supported status
ResizableSheet supports 3 statuses, .hidden, .medium and .large.
In default setting, the all statuses are supported, but you can stop to support any statuses.
view.resizableSheet($state) { builder in
builder.content { context in
Text("Text").frame(height: 300)
}
.supportedState([.medium])
}
Multi Sheets
ResizableSheet supports multiple sheets.
By adding id, ResizableSheet can show multiple sheets.
struct SomeSheet: View {
@State var stateA: ResizableSheetState = .hidden
@State var stateB: ResizableSheetState = .hidden
var body: some View {
Button("Show sheet A") {
stateA = .medium
}
.resizableSheet($stateA, id: "A") { builder in
builder.content { context in
Button("Show sheet B") {
stateB = .medium
}.frame(height: 300)
}
}
.resizableSheet($stateB, id: "B") { builder in
builder.content { context in
Button("remove all sheet") {
stateA = .hidden
stateB = .hidden
}.frame(height: 200)
}
}
}
}
ResizableScroolView (TrackableScrollView)
ResizableSheet includes ResizableScrollView.
The view synchronises the offset with ResizableSheet.
Tips: Using ResizableScroolView is recommended because you don’t need to calculate the medium size.
view.resizableSheet($state) { builder in
builder.content { context in
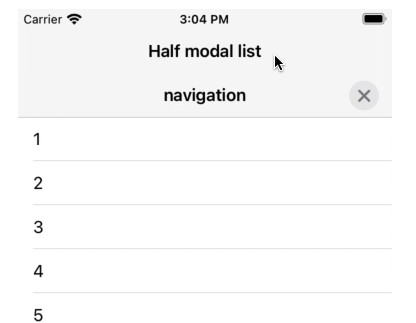
ResizableScrollView(context: context) {
// These views are shown in medium size and large size.
ForEach(0..<5) { index in
Text("\(index)")
.padding()
}
} additional: {
// These views are shown in only large size.
ForEach(5..<100) { index in
Text("\(index)")
.padding()
}
}
}
}
EmptyBackground
By passing EmptyView as background, user can control both the parent view and the sheet.
struct SomeView: View {
@State var counter = 0
@State var state: ResizableSheetState = .hidden
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("\(counter)")
.font(.largeTitle)
Button("count") {
counter += 1
}
Spacer()
Button("Show sheet") {
state = .medium
}
Spacer()
}
.resizableSheet($state) { builder in
builder.content { context in
Content(counter: $counter).frame(height: 300)
}
.background { _ in EmptyView() } // add this line
}
}
struct Content: View {
@Binding var counter: Int
var body: some View {
VStack {
Spacer()
Text("\(counter)")
.font(.largeTitle)
Button("reset") {
counter = 0
}
Spacer()
}
}
}
}